Updated September 22, 2021
Japan
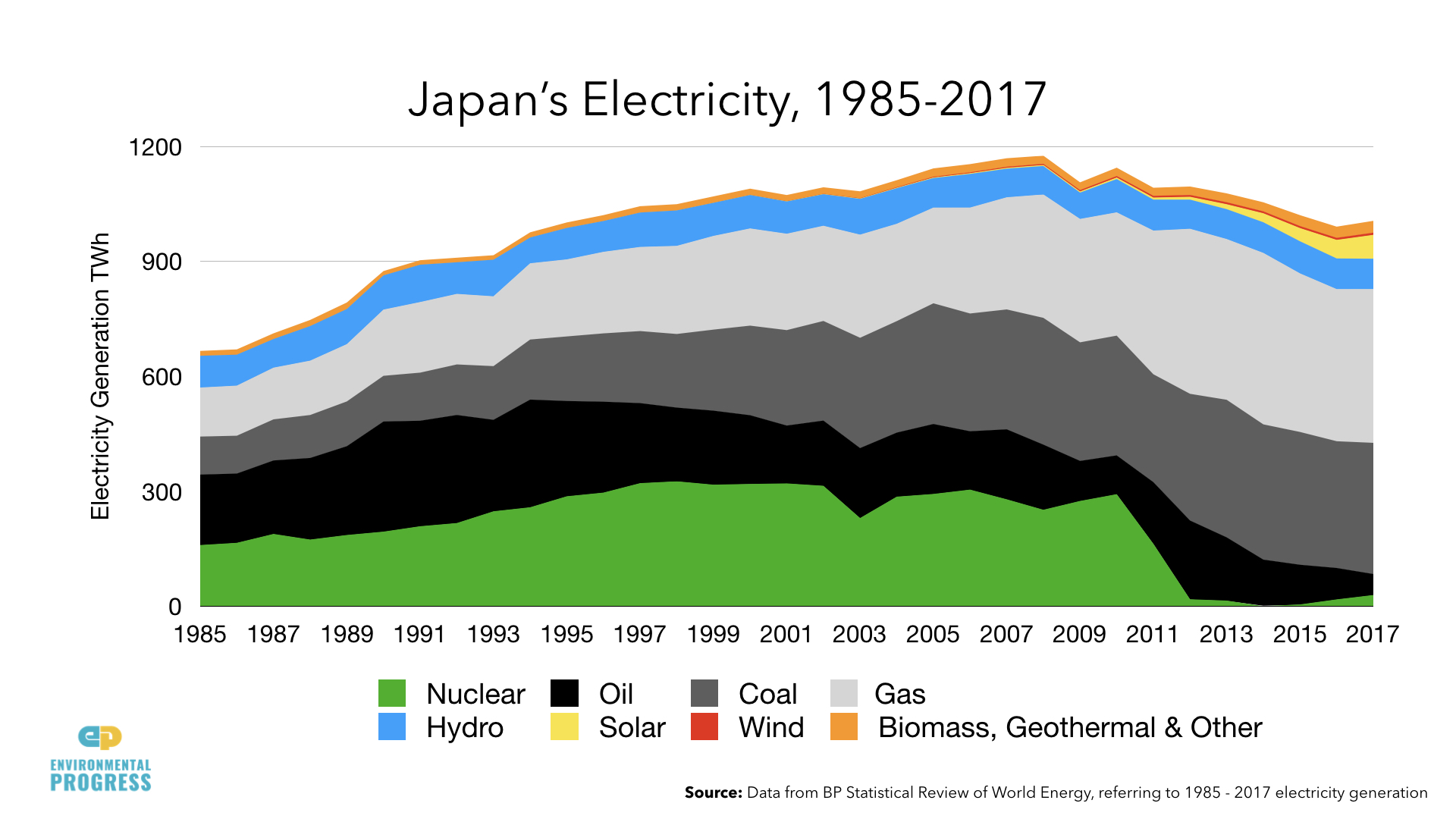
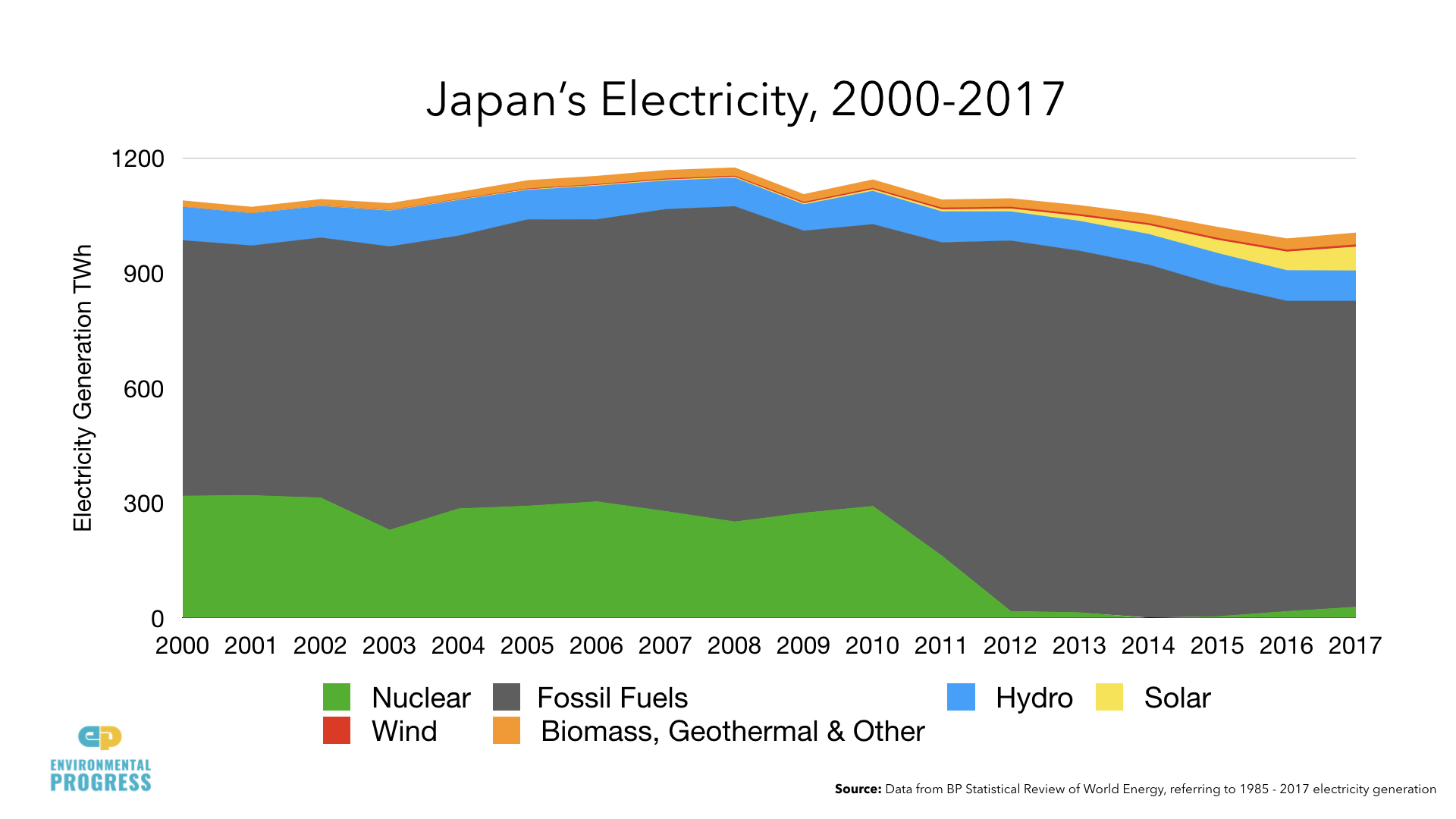
Out of 42 reactors that are operable and potentially able to restart, only five have been restarted since Fukushima. 24 are in the process of restart approvals.
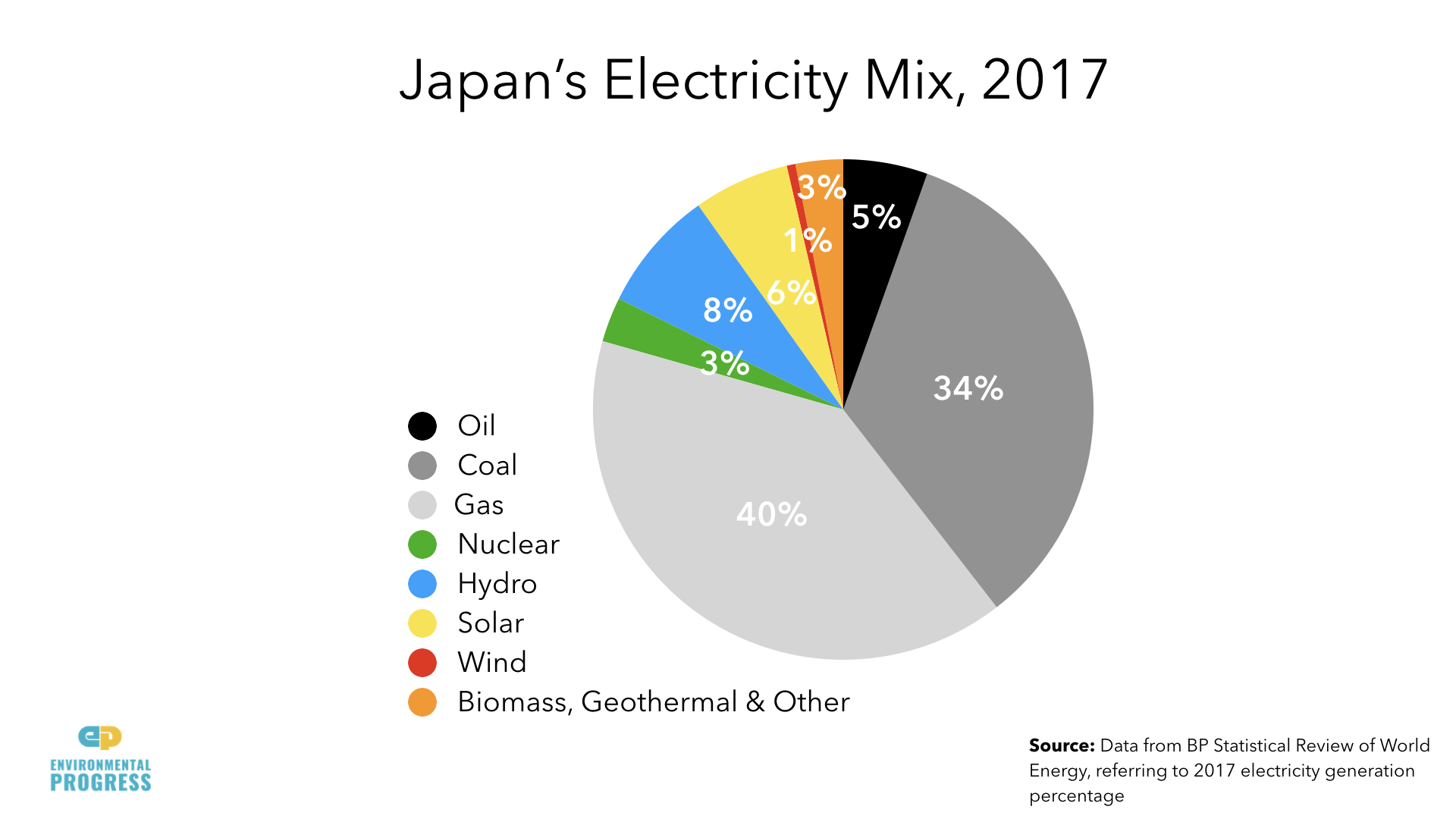
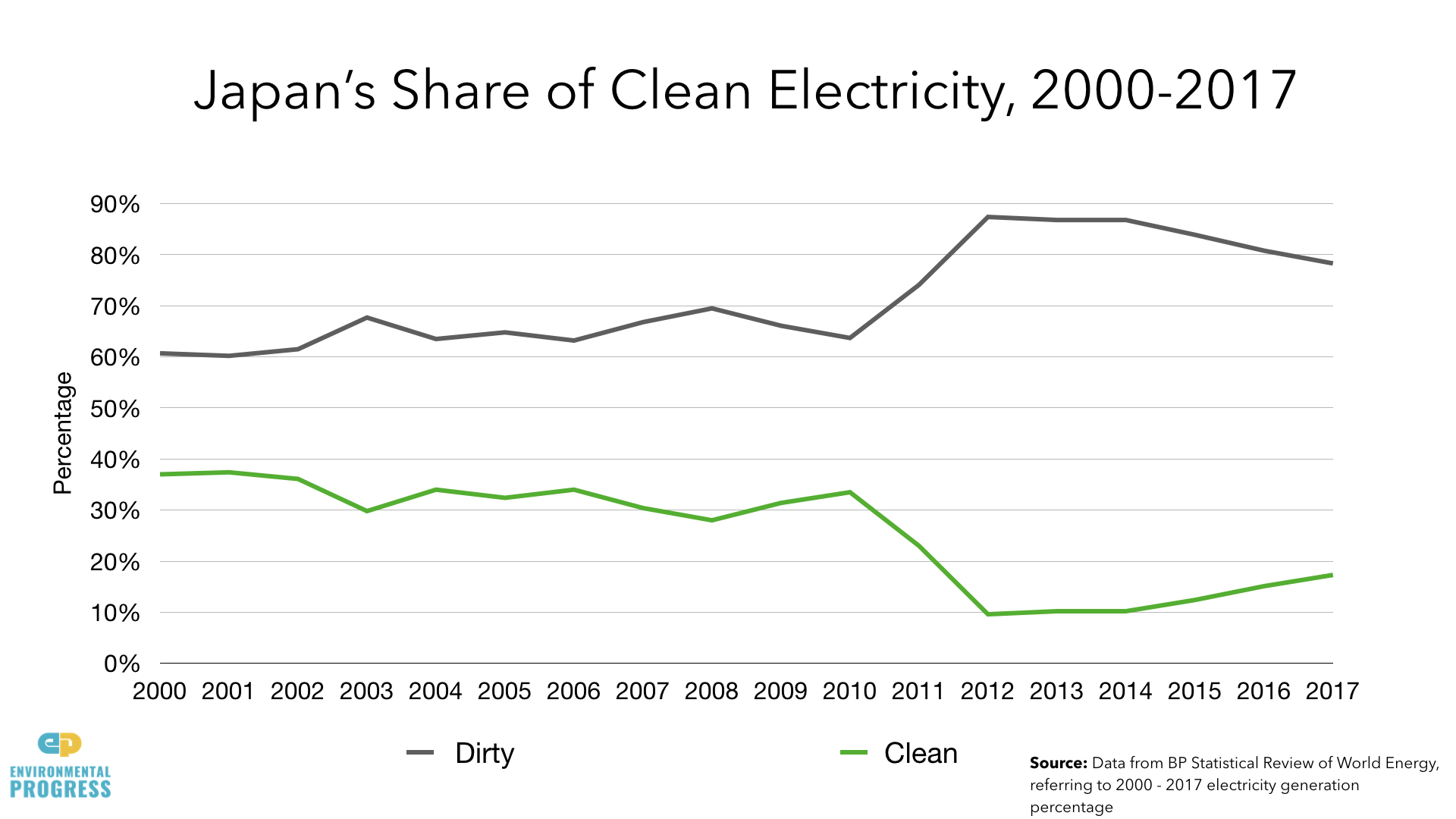
Japan's share of clean electricity fell from 34 percent to 16 percent between 2010 and 2015.
The Japanese government, in the view of Chernobyl expert Geraldine Thomas and other radiation experts, contributed to the widespread view of radiation as a super-potent toxin by failing to return residents to the Fukushima province after the accident, and for reducing radiation in soil and water to unnecessarily low levels.
Japan must import about 84 percent of its energy, much of it in the form of fossil fuels.
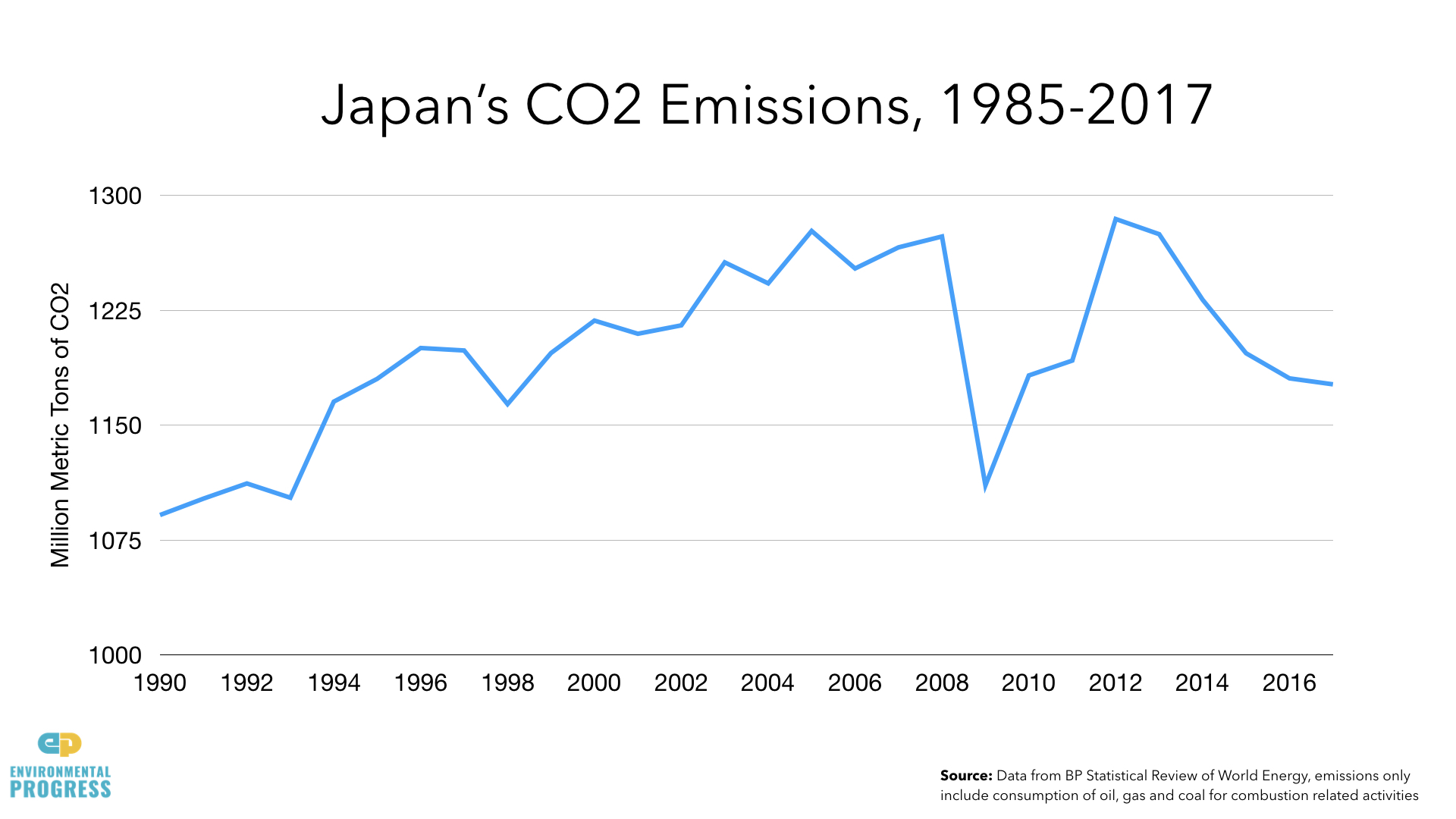
Japan’s trade balance went from being a surplus to a deficit from 2010 to 2013 due to increased fossil fuel imports. This deficit reached 11.47 trillion yen in 2013. Recent surpluses in early 2017 are due to a growth in auto part shipments.
Japan’s nuclear industry continues to look for ways to get back into exports. Recent events in the USA, such as the removal of the US Development Finance Corporation’s ban on nuclear export financing, has raised hopes that Mitsubushi reactor vessels and steam generators (in AP1000s) and Hitachi BWRs (in partnership with GE) might return as options for countries adding nuclear capacity.
Banner photo credit: Karl Baron